With its excellent comprehensive performance, GYHTY optical cable has become a core infrastructure for modern communication network construction. With continuous innovations in materials science and communication technology, GYHTY optical cable will play a more critical role in smart grids, rail transit, industrial Internet and other fields, driving the development of communication networks towards high-speed, intelligent and ubiquitous directions.
Product Description
Colored optical fibers are placed into a loose tube made of high modulus material, which is then filled with thixotropic water-blocking gel. The center of the cable core contains a glass fiber reinforced plastic(FRP). The loose tube(and filling rope)is twisted around the central reinforcing core to form a circular cable core. Gaps in the cable core are filled with water-blocking gel, and then extruded with a polyethylene inner sheath. This is followed by an outer sheath made of aramid yarn, extruded with polyethylene to complete the cable.
Product Features
The material of the loose tube itself has good resistance to hydrolysis and high strength.
◆Possesses good mechanical performance and temperature characteristics.
◆Aramid reinforcing elements enhance the cable's tensile strength.
◆Filled with thixotropic gel inside the tube, providing crucial sealing protection to the optical fibers.
◆PE sheath has excellent resistance to ultraviolet radiation.
◆Single non-metallic central reinforcing core.
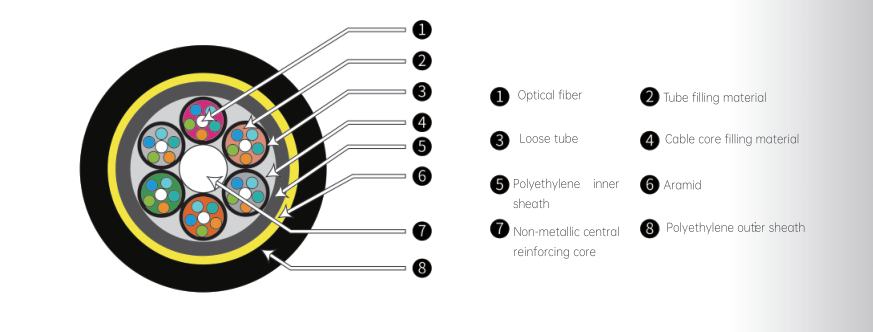
Application: Ducts, Aerial, Direct Burial
GYHTY optical cable is a type of outdoor communication cable with a stranded-layer structure and non-metallic strength member. It is designed to combine high reliability with environmental adaptability, making it particularly suitable for scenarios with strong electromagnetic interference, frequent lightning strikes, and strict non-metallic requirements. This document provides a detailed analysis of its structural design, performance parameters, application scenarios, and technical innovations.
Material Selection: Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) is used as the central strength member, with an elastic modulus of over 100 GPa. It combines the rigidity of metallic materials with the insulation properties of non-metallic materials.
Mechanical Properties: The tensile strength of a single FRP rod is ≥1200 MPa, providing basic tensile resistance for the cable while avoiding the risk of induced current in high-electricity environments.
Structural Optimization: The surface of the FRP rod is specially treated to form a tight stranded structure with surrounding loose tubes, ensuring uniform stress distribution and reducing micro-bending losses in the optical fibers.
Loose Tube Material: Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT) is used, with a glass transition temperature of ≥220°C, maintaining stable mechanical properties in the temperature range of -40°C to +70°C.
Fiber Protection Mechanism:
Special ointment (dropping point ≥120°C) is filled inside the tube, with a dynamic viscosity of 5000-8000 mPa·s at 25°C, effectively buffering external mechanical shocks.
The fiber excess length is controlled at 0.5%-0.8%, achieved through precise stranding processes, ensuring that the fiber strain ≤0.05% under temperature changes.
Cable Core Structure:
Loose tubes and filling ropes are stranded around the central strength member in an SZ stranding manner, with a stranding pitch of 20-30 times the cable diameter, forming a compact circular structure.
The gaps in the cable core are filled with water-blocking yarn (water absorption capacity ≥20 times its own weight), with a longitudinal water-blocking rate ≤0.1 mL/m, meeting the requirements of IEC 60794-1 standard.
Sheath Design:
The inner sheath is made of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) with a thickness of ≥1.5 mm and an environmental stress cracking resistance time (ESCR) of ≥1000 hours.
An aramid yarn layer is added to the outer sheath. The aramid has a density of 1.44 g/cm³ and a breaking strength of ≥2800 MPa, increasing the short-term tensile capacity of the cable to over 1500 N.
Attenuation Characteristics:
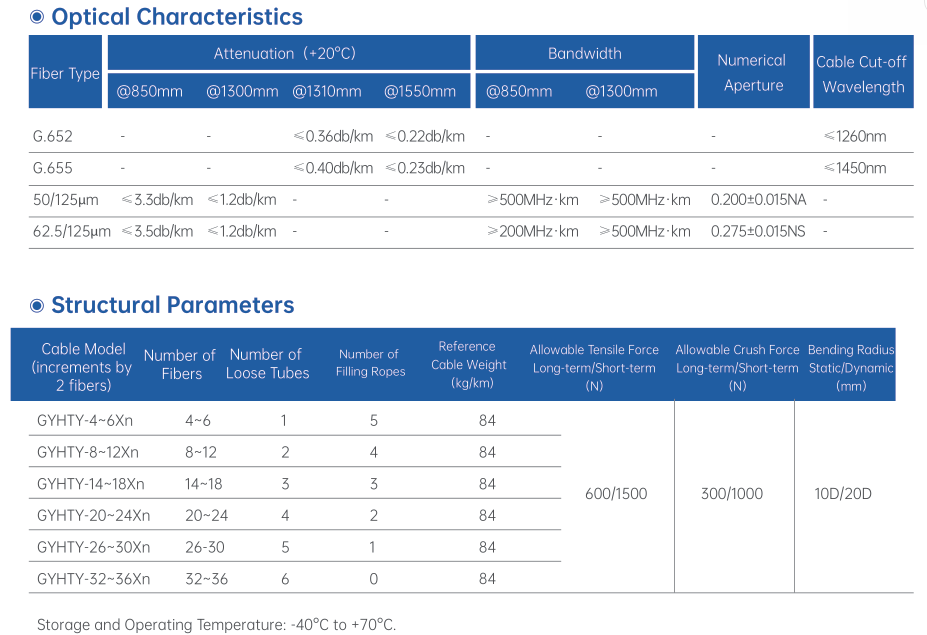
Single-mode fiber (G.652D): Attenuation ≤0.36 dB/km at 1310 nm wavelength and ≤0.22 dB/km at 1550 nm wavelength.
Multi-mode fiber (50/125 μm): Attenuation ≤3.0 dB/km at 850 nm wavelength and ≤1.0 dB/km at 1300 nm wavelength.
Dispersion Characteristics:
Cut-off Wavelength: ≤1260 nm for single-mode fiber and ≤1480 nm for multi-mode fiber, ensuring pure mode within the working wavelength range.
Tensile Performance:
Long-term allowable tensile force: 600 N (for 8-12 core cables), short-term allowable tensile force: 1500 N, meeting the requirements of YD/T 901 standard.
The aramid yarn layer extends the dynamic tensile fatigue life of the cable to ≥100,000 cycles (load ±20% of the rated tensile force).
Compressive Performance:
Bending Performance:
Material Innovation:
Using basalt fiber to replace part of FRP, raising the temperature resistance limit of the cable to +120°C, suitable for high-temperature industrial scenarios.
Developing nano-composite sheath materials with an ultraviolet absorption rate increased to 98%, extending the anti-aging life to 50 years.
Structural Innovation:
Integrating fiber optic sensors to 实现 distributed temperature monitoring (DTS) with a temperature measurement accuracy of ±1°C and a positioning accuracy of ±1 m.
Adopting a micro-loose tube design (inner diameter 2.5 mm), increasing the core density to 288 cores/12 mm outer diameter to meet the requirements of 5G fronthaul.
Process Innovation:
Applying laser welding technology to increase the bonding strength between FRP and the sheath to 50 N/cm, reducing the risk of interface peeling.
Introducing an AI vision inspection system to improve the control accuracy of fiber excess length to ±0.05%, with an attenuation fluctuation of ≤0.02 dB/km.
Interconnection Project of 110 kV Substations in Southern Power Grid:
Communication System of Beijing-Shanghai High-Speed Railway:
Smart Grid Demonstration Project in Xiongan New Area:
Daily Maintenance Points:
Test the cable grounding resistance (≤10 Ω) and insulation resistance (≥10⁴ MΩ·km) quarterly.
Conduct OTDR tests annually with an attenuation change threshold of 0.1 dB/km and a positioning accuracy of ±5 m.
Common Fault Handling:
Fiber Breakage: Repair using a fusion splicer (fusion loss ≤0.05 dB) in conjunction with heat-shrinkable sleeves, taking ≤30 minutes per point.
Sheath Damage: Repair using special repair patches (tensile strength ≥20 MPa), restoring the pressure resistance to 90% of the original sheath.
Core Number Selection:
Environmental Adaptation:
Strong Electricity Areas: Prioritize aramid-reinforced GYHTY with a metal component content of ≤0.1%.
Humid Areas: Adopt a fully water-blocking structure with water-blocking yarn water absorption capacity ≥20 times its own weight.
Economic Analysis:
Short-Term Projects: Select economical GYHTY (unit price approximately 8 yuan/meter) to meet basic communication needs.
Long-Term Projects: Use high-reliability GYHTY (unit price approximately 12 yuan/meter) to reduce maintenance costs.
Technological Evolution Direction:
Develop Space Division Multiplexing (SDM) technology to 突破 the single-cable capacity of 1 Pb/s, supporting ultra-high-speed transmission in 6G networks.
Integrate terahertz communication modules to 实现 optical cable-wireless fusion transmission with a coverage radius of ≤100 m.
Application Expansion Areas:
Deep-Sea Communication: Through armor optimization (double-layer stainless steel tape), withstand a pressure depth of 3000 meters, supporting the construction of undersea observation networks.
Space Communication: Use high-temperature-resistant sheaths (temperature resistance +200°C) to meet the interconnection requirements of near-Earth orbit satellite ground stations.
Note:
a.The suffix Xn in the model indicates the selected fiber type, see Yangtze Fiber Model Explanation for details.
b.The color arrangement of the loose tube and fibers can be found in the chromatogram.
c.The minimum thickness of the polyethylene sheath is 1.5mm.
d.The cable should not be stored in open-air environ- ments for more than 6 months, otherwise the spool may
be damaged.
e.This document is for reference only and cannot be used as an attachment to the contract. For detailed product
information, please contact our sales staff.











