With its flexible branch structure, low-loss optical performance, reliable environmental adaptability and strict standard certification, BOC optical cable has become an indispensable part of modern communication networks. From FTTH to data centers, from base station connections to large-scale events, BOC optical cables, with their excellent parameter characteristics, provide a solid support for efficient and stable optical communication. With the development of 5G, 8K and other technologies, BOC optical cables will play a key role in more high-bandwidth and high-density scenarios.
Product Description
The multi-purpose branch cable utilizes single-core optical cable (with 900μm tight-buffered optical fiber and aramid strength member) as subunits, with a non-metallic central strengthening core. The cable subunits are twisted around the central strengthening core to form the cable core. Finally, a layer of
polyvinyl chloride (PVC) sheath is extruded on the outside. Alternatively, a low smoke zero halogen (LSZH) material sheath can be provided according to customer requirements.
Product Feature
The non-metallic strengthening core enables the optical cable to withstand greater tensile forces.
◆ Aramid yarn strength members provide outstanding tensile performance for the cable.
◆ The outer sheath material offers corrosion resistance,waterproofing,flame resistance,and environmental friendliness.
Product Applications
• Indoor comprehnsive cabling
• Backbone cabling optical fiber cable for buildings
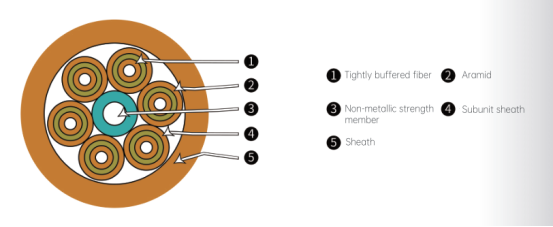
Multi Purpose Break out Cable
Indoor optical cable
Delivery Length
Recommended Length: 2000m; other lengths can be provided according to customer requirements.
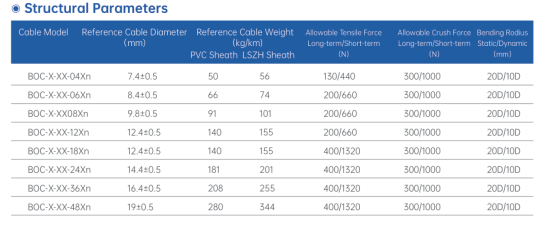
I. Structural Parameter Characteristics
1. Number of Fiber Cores and Layout
BOC optical cables usually adopt a stranded structure. The main optical cable contains 24 to 144 fiber cores, and branches out multiple sub-cables. For example, the Hanxin BOC-24 model contains 24 fiber cores, with a diameter of 13.8±0.5mm and a weight of 140kg/km; while the BOC-144 model increases the number of cores to 144, with a diameter of 36.5±0.5mm and a weight of 870kg/km. This design is suitable for scenarios requiring multiple branches such as FTTH (Fiber to the Home) and 3G base stations, where signals are distributed to multiple users or devices through splitters.
2. Fiber Type and Tight-Buffered Design
The sub-units use Φ900μm tight-buffered fibers, which are divided into multimode (50/125μm or 62.5/125μm) and single-mode (G.652, G.655) types. Multimode fibers are suitable for short-distance high-speed transmission, such as a bandwidth of ≥500MHz·km at 850nm wavelength; single-mode fibers (such as G.652) have an attenuation of ≤0.45dB/km at 1310nm wavelength, which is suitable for long-distance transmission. Tight-buffered fibers are easy to strip and splice, improving construction efficiency.
3. Reinforcement Elements and Mechanical Support
Non-metallic central strength members (such as FRP) combined with aramid yarn or phosphated steel wire provide excellent tensile performance. For example, the long-term tensile strength of Changfei BOC optical cable is 200N, and the short-term can reach 660N; Corning DualDrop optical cable uses a water-swellable insulated strength member, with a long-term tensile strength of 300N and a short-term of 1000N. Aramid yarn can also enhance the lateral pressure resistance. For example, the long-term crushing strength of Hanxin BOC optical cable is 300N/100mm, and the short-term is 1000N/100mm.
4. Sheath Material and Protection Design
The outer sheath is made of PVC or LSZH (low smoke zero halogen) material. PVC sheath is waterproof and corrosion-resistant, suitable for general environments; LSZH sheath has excellent flame retardancy, meeting the IEC 60332-3C standard, and does not produce toxic smoke when burned, making it suitable for scenarios with high fire safety requirements such as indoor shafts. Some models are also coated with anti-rat paint on the outer side of the sheath to enhance the ability to resist damage from rodents.
5. Branch Structure Design
BOC optical cables are divided into parallel branch and integrated branch:
Parallel branch: The main cable and branches are in a parallel structure, and the sub-cables are separated through intermittent cuts, which is suitable for scenarios with more branches, such as branching multiple user lines from the main cable in FTTH.
Integrated branch: The sub-cables are integrated into a circular sheath, with a smaller outer diameter (≤20mm), suitable for high-density wiring, such as indoor comprehensive wiring or FTTH terminal box connections.
II. Optical Characteristic Parameter Characteristics
1. Transmission Rate and Wavelength
BOC optical cables support multiple transmission rates:
Basic models (such as Changfei BOC-48B1) have a transmission rate of 1000Mbps, meeting the needs of enterprise local area networks.
High-end models (such as FS 100G QSFP28 active branch optical cables) support 100Gbps high-speed transmission, used for connections between racks in data centers, with a transmission distance of up to 70 meters.
The transmission wavelength is selected according to the fiber type:
Multimode fiber: 850nm (short distance) and 1300nm (medium distance), with bandwidths of 500MHz·km and 1000MHz·km respectively.
Single-mode fiber: 1310nm (attenuation ≤0.45dB/km) and 1550nm (attenuation ≤0.25dB/km), suitable for long-distance trunk lines.
2. Attenuation and Dispersion Control
Attenuation characteristics: The attenuation of single-mode fiber at 1550nm wavelength can be as low as 0.2dB/km or less, and the attenuation of multimode fiber at 1310nm is ≤0.5dB/km. The fusion splicing loss is ≤0.06dB/point, and the cold splicing loss is ≤0.15dB/point, which needs to reserve a margin in the link design.
Dispersion characteristics: The dispersion of single-mode fiber (such as G.652) at 1550nm is ≤18ps/(nm·km). By optimizing the waveguide structure, it can be further reduced, supporting transmission at rates above 10Gbps for more than 50 kilometers.
3. Splitting Loss and Link Design
When BOC optical cables are split, splitter insertion loss and connector loss need to be considered:
The insertion loss of the splitter increases with the increase of the splitting ratio. For example, the insertion loss of a 1:64 splitting ratio is about 19.8dB (box-type splitter), and the insertion loss of a plug-in splitter is slightly higher by 0.2dB.
The total attenuation of the link is calculated as:///(A_{/text{total}} = A_{///text{fiber}} + A_{///text{splitter}} + A_{///text{connector}} + A_{///text{additional}}///)Among them, the fiber attenuation is calculated at 0.35dB/km, and the connector loss is calculated at 0.5dB/piece (active connection) or 0.1dB/point (fusion splicing).
III. Environmental Performance Parameter Characteristics
1. Temperature Adaptability
Operating temperature: -20℃~+60℃, installation temperature -5℃~+50℃, suitable for areas with large temperature differences between the north and the south.
Temperature cycle test: After the optical cable is cycled in the range of -40℃~+70℃, the sheath has no cracks, and the fiber attenuation change is ≤0.1dB.
2. Waterproof and Moisture-proof
The sheath material (PVC/LSZH) itself is waterproof, and the tight-buffered fiber structure prevents moisture penetration. Tests show that when the optical cable is immersed in water under 0.1bar water pressure for 24 hours, the water seepage length is ≤3 meters.
The water-blocking tape layer (double-sided non-woven fabric) and fiber paste filling further enhance moisture-proof performance, suitable for pipelines or humid environments.
3. UV Resistance and Weather Resistance
Outdoor BOC optical cable sheaths are added with UV-resistant additives. After testing according to the IEC 62133 standard, the sheath has no cracks, and the fiber attenuation change is ≤0.05dB.
UV-resistant sheaths can extend the outdoor service life to more than 20 years, suitable for overhead or direct burial laying.
4. Flame Retardancy and Environmental Protection
LSZH sheath meets the IEC 60332-3C standard. In the vertical burning test, the flame spread is ≤2.5 meters, and the smoke density is ≤75% (IEC 61034).
Halogen-free materials do not release acid gas when burned, meeting the EU RoHS directive, suitable for scenarios with high environmental protection requirements such as medical treatment and data centers.
IV. Mechanical Performance Parameter Characteristics
1. Tensile Strength
Long-term tensile strength: 200N (BOC-24) to 1000N (Corning DualDrop), ensuring that the fiber is not damaged by stretching during laying.
Short-term tensile strength: 660N (BOC-24) to 2000N, which can withstand temporary traction or accidental tension.
2. Crushing and Impact Resistance
Long-term crushing strength is 300N/100mm, short-term is 1000N/100mm, suitable for resisting external pressure when laid in pipelines or trunking.
Impact resistance test: After 1J energy impact, the fiber attenuation change is ≤0.1dB, and the sheath has no visible damage.
3. Bending Radius
Static bending radius: 10 times the outer diameter of the optical cable (such as BOC-24 static bending radius 138mm), dynamic bending radius 20 times the outer diameter.
Some models (such as Corning ClearCurve) use bend-resistant fibers, and the static bending radius can be reduced to 30mm, suitable for wiring in narrow spaces.
4. Wear Resistance and Anti-aging
The surface hardness of the sheath is ≥Shore D80, and there is no obvious wear after the wear test.
After 1000 hours of aging test (85℃/85%RH), the retention rate of the tensile strength of the sheath is ≥80%.
V. Standard and Certification Parameter Characteristics
1. Industry Standards
Domestic standards: Comply with YD/T 1258.4 (indoor optical cables), YD/T 1997 (access network optical cables), etc., to ensure product quality and compatibility.
International standards: Meet IEC 60794-2-10 (mechanical properties), IEC 60794-1-22 (environmental properties), etc., supporting global market applications.
2. Certification Requirements
Flame retardant certification: LSZH sheath passes IEC 60332-3C, and PVC sheath passes UL OFNR (vertical burning) or OFNP (ventilation duct) certification.
Environmental protection certification: Complies with RoHS 2011/65/EU, free of lead, mercury and other harmful substances.
Performance certification: Some models pass GR-409 (Telcordia) or ICEA-596, proving their reliability and long-term stability.
VI. Application Scenarios and Typical Cases
1. FTTH Access Network
In FTTH, BOC optical cables branch out multiple sub-cables from the main cable to user terminals, reducing the number of connectors and the probability of failures. For example, a branch optical cable with a 1:64 splitting ratio can cover 64 households, and the total attenuation of the whole process is controlled within 25dB.
2. 5G Base Station Connection
When 5G base stations are densely deployed, BOC optical cables are used to branch from the core network to multiple base stations, shortening the transmission distance (such as 200 meters) and supporting 10Gbps fronthaul signal transmission.
3. Data Center Interconnection
100G active branch optical cables (such as FS QSFP28 to 4LC) are used for connections between racks, with a transmission distance of 70 meters, power consumption <2.2W, supporting high-density wiring.
4. Large-scale Event Communication
During the Wuhan Military World Games, BOC optical cables were used in the remote production control center to transmit camera signals to the IBC (International Broadcasting Center) through optical cables, realizing real-time switching of 4K/8K signals.
Note:
This document is for reference only and cannot be used as an attachment to the contract.
For detailed product information, please contact our sales staff.









