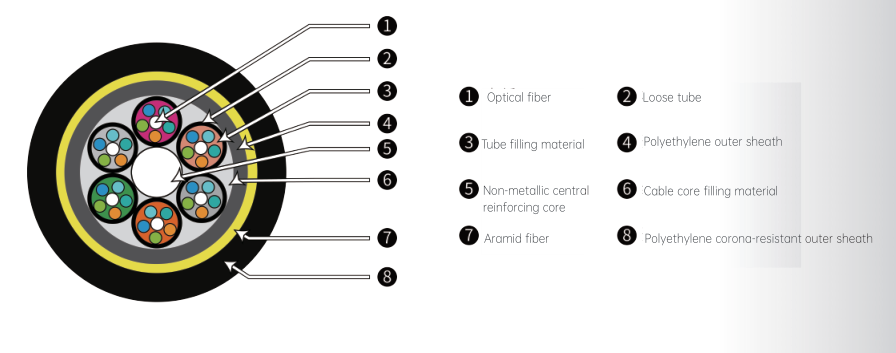
Colored optical fibers are placed into a loose tube made of high-modulus material, which is filled with thixotropic water-blocking gel. The core of the cable consists of a metal strength member. The loose tube(and filling rope)is twisted around the central strength member to form a circular cable core. Gaps within the cable core and between the cable core and the steel tape are filled with water-blocking gel. After longitudinal wrapping with coated aluminum tape and extrusion of a polyethylene inner sheath, the cable is wrapped with coated steel tape and extruded with a flame-retardant outer sheath
Product Description
Colored optical fibers are placed into a loose tube made of high-modulus material, which is filled with thixotropic water-blocking gel. The core of the cable consists of a metal strength member. The loose tube(and filling rope)is twisted around the central strength member to form a circular cable core. Gaps within the cable core and between the cable core and the steel tape are filled with water-blocking gel. After longitudinal wrapping with coated aluminum tape and extrusion of a polyethylene inner sheath, the cable is wrapped with coated steel tape and extruded with a flame-retardant outer sheath
Product Features
◆Utilizes AT sheath, providing strong resistance to electric corrosion.
◆Lightweight with high tensile strength, enabling long span installations.
◆Exhibits excellent resistance to tension and temperature variations.
Optical Characteristics
| Fiber Type | Attenuation(+20℃) | Bandwidth | Numerical | Cable Cut-off |
| @850mm | @1300mm | @1310mm | @1550mm | @850mm | @1300mm | Aperture | Wavelength |
| G.652 |
|
| ≤0.36db/km | ≤0.22db/km |
|
|
| ≤1260nm |
| G.655 | - | - | ≤0.40db/km | ≤0.23db/km | - |
| - | ≤1450nm |
| 50/125μm | ≤3.3db/km | ≤1.2db/km | - | - | ≥500MHz ·km | ≥500MHz ·km | 0.200±0.015NA | - |
| 62.5/125μm | ≤3.5db/km | ≤1.2db/km | - |
| ≥200MHz ·km | ≥500MHz ·km | 0.275±0.015NS | - |
Mechanical Performance Parameters:
Rated Tensile Strength (RTS): Also known as ultimate tensile strength or breaking force, it refers to the calculated value of the sum of the strengths of the load-bearing sections (mainly aramid fibers). The actual breaking force should be ≥95% of the calculated value, that is, the fracture of any component in the optical cable is judged as cable breaking. This parameter is related to many control values, such as tower strength, tension-resistant hardware, anti-vibration measures, etc. Usually, the Maximum Allowable Tension (MAT) is approximately equivalent to 40% of RTS.
Maximum Allowable Tension (MAT): Refers to the tension that the optical cable is subjected to when theoretically calculating the total load under the designed meteorological conditions. Under this tension, the fiber strain should be ≤0.05% (stranded type) and ≤0.1% (central tube type) without additional attenuation. Based on this parameter, meteorological conditions, and controlled sag, the allowable span of the optical cable under these conditions can be calculated, which is an important basis for sag-tension-span calculation.
Annual Average Operating Tension (EDS): Sometimes called daily average stress, it refers to the tension that the optical cable is subjected to when theoretically calculating the load under no wind, no ice, and annual average temperature. It can be considered as the long-term operating average tension of ADSS. EDS is generally (16-25)% of RTS. Under this tension, the optical fiber should have no strain, no additional attenuation, and be in a very stable state. At the same time, EDS is also the fatigue aging parameter of the optical cable, which determines the anti-vibration design of the optical cable.
Ultimate Operating Tension (UES): Also known as special use tension, it refers to the maximum tension that the optical cable may be subjected to when the load exceeds the design load during the effective life of the optical cable. It means that the optical cable is allowed to be overloaded for a short time, and the optical fiber can bear strain within a limited allowable range. Usually, UES should be >60% of RTS. Under this tension, the fiber strain is <0.5% (central tube) and <0.35% (stranded), and the optical fiber will have additional attenuation, but after the tension is released, the optical fiber should return to normal. This parameter ensures the reliable operation of the ADSS optical cable during its service life.
Compressive Strength: ADSS optical cables need to have a certain compressive strength to withstand external pressure that may be encountered during laying and operation. For example, the ADSS-12B1-AT-400 optical cable from Hunan Han Cable Communication has a long-term compressive strength of 1100N/100mm and a short-term compressive strength of 2200N/100mm.
Wind Deflection Angle: The wind deflection angle of ADSS optical cables is relatively large. At a wind speed of 30m/s, the wind deflection angle can reach 80°, while the wind deflection angle of the conductor is only about half of that of the optical cable. This is because its tensile strength is borne by aramid fibers, and the elastic modulus of aramid fibers is more than half that of steel, resulting in the sag of ADSS optical cables being more sensitive to changes in external loads.
Structural Parameters:
Central Reinforcement: Generally made of Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP), which has the characteristics of high strength, corrosion resistance, and good insulation performance. Its diameter is usually about 2.0-2.3mm. For example, the diameter of the central reinforcement FRP of the ADSS-12B1-AT-400 optical cable is 2.0mm, and that of the ADSS-24B1-AT-600 optical cable is 2.3mm.
Loose Tube: Made of high-modulus plastic, filled with water-blocking ointment to protect the optical fiber. The outer diameter of the loose tube is generally between 1.90-2.05mm. The number of loose tubes and the number of fiber cores in each tube vary with different types of optical cables. For example, the ADSS-12B1-AT-400 optical cable has 2 loose tubes, with 6 fiber cores in each tube; the ADSS-48B1-PE-400 optical cable has 6 loose tubes, with 8 fiber cores in each tube.
Mechanical Reinforcement Layer: Usually composed of aramid fibers, which have the characteristics of high strength and high modulus and are the main tensile elements of ADSS optical cables. The area of aramid fibers varies according to the rated tensile strength of the optical cable. For example, the aramid area of the ADSS-12B1-AT-400 optical cable is 26mm², and that of the ADSS-24B1-AT-600 optical cable is 32mm².
Outer Sheath: Generally made of polyethylene (PE) or anti-tracking (AT) sheath material. PE sheath is used for power lines below 110kV, and AT sheath is used for power lines above 110kV. The thickness of the outer sheath is generally about 1.7-1.8mm, which has the functions of protecting the internal structure of the optical cable, preventing moisture intrusion, and resisting tracking corrosion.
Cable Core Structure: There are mainly two types: central tube type and stranded type. The central tube structure places the optical fiber in a PBT tube filled with water-blocking ointment with a certain excess length, then wraps aramid yarn and extrudes the sheath. This structure is easy to obtain a small diameter, has a small ice-wind load, and is relatively light in weight, but the excess length of the optical fiber is limited. The stranded structure winds the optical fiber loose tube around the central reinforcement with a certain pitch, then extrudes the inner sheath, wraps aramid yarn, and the outer sheath. The stranded structure is easy to obtain a safe excess length of the optical fiber and has advantages in medium and large span applications.
Optical Fiber Parameters:
Optical Fiber Model: The commonly used optical fiber model is G652D, which has good transmission performance and compatibility.
Mode Field Diameter: For G652D optical fiber, the mode field diameter is 8.6-9.5±0.7μm. The consistency of the mode field diameter is crucial to the transmission performance of the optical fiber.
Cladding Diameter: The cladding diameter is generally 125.0±1μm. The accuracy of the cladding diameter affects the connection performance between the optical fiber and other optical devices.
Concentricity Error: The maximum concentricity error is 0.8μm. The smaller the concentricity error, the more stable the transmission performance of the optical fiber.
Cladding Non-Circularity: The maximum cladding non-circularity is 2.0%. Cladding non-circularity will affect the bending resistance and connection loss of the optical fiber.
Cable Cutoff Wavelength: Generally, the maximum is 1260μm. The cable cutoff wavelength determines the transmission characteristics of the optical fiber at a specific wavelength.
Attenuation Coefficient: At 1310nm wavelength, the maximum attenuation coefficient is 0.36dB/km; at 1550nm wavelength, the maximum attenuation coefficient is 0.22dB/km. The attenuation coefficient is an important indicator to measure the transmission performance of the optical fiber. The smaller the attenuation, the longer the signal transmission distance.
Electrical Performance Parameters:
Insulation Performance: ADSS optical cable uses all dielectric materials, has good insulation performance, does not conduct electricity, and can avoid electric shock accidents and electrical interference in high-voltage and strong electric environments.
Tracking Resistance Performance: Since ADSS optical cable operates in a strong electric field, the outer sheath needs to have tracking resistance performance. For power lines above 110kV, AT sheaths are usually used to reduce tracking corrosion on the surface of the optical cable caused by strong electricity.
Anti-Electromagnetic Interference Performance: ADSS optical cable is a non-metallic dielectric, not affected by electromagnetic interference, and can stably transmit signals near high-voltage transmission lines, suitable for places with complex electromagnetic environments.
Other Parameters:
Optical Cable Outer Diameter: The outer diameter of ADSS optical cable is generally about 12.9-14.5mm. For example, the outer diameter of ADSS-12B1-AT-400 optical cable is 12.9mm, and that of ADSS-24B1-AT-600 optical cable is 14.5mm. A small cable diameter can reduce the impact of ice and wind on the optical cable and also reduce the load on the tower and support.
Optical Cable Weight: The weight of the optical cable is relatively light, and the mass per unit length is generally about 133-178kg/km. The specific weight is related to the structure, core number, and rated tensile strength of the optical cable. For example, the unit length mass of ADSS-100-1 optical cable is ≤133kg/km, and the weight of ADSS-24B1-AT-600 optical cable is 178kg/km.
Minimum Bending Radius: The minimum bending radius of ADSS optical cable is generally 20 times the cable diameter during operation and 30 times the cable diameter during laying. For example, the minimum bending radius of ADSS-12B1-AT-400 optical cable during operation is 220mm, and during laying is 360mm.
Applicable Temperature Range: Generally, the laying temperature range of ADSS optical cable is -15℃ to +60℃, and the transportation and operation temperature range is -40℃ to +70℃. The optical cable should be able to maintain the stability of its mechanical and optical properties in different temperature environments.
Optical Fiber Excess Length: The excess length of the optical fiber is generally controlled at about 0.5%-0.7%. The precisely controlled excess length of the optical fiber ensures that the optical cable has good tensile performance and temperature characteristics. When the optical cable is stretched or the temperature changes, the optical fiber can freely expand and contract within the excess length range to avoid additional attenuation.
Application: Ducts, Aerial
Note:
a.The suffix Xn in the model indicates the selected fiber d.The cable should not be stored in open-air
type,see Yangtze Fiber Model Explanation for details. environments for more than 6 months,otherwise the
b.The color arrangement of the loose tube and fibers can spool may be damaged.
be found in the chromatogram.e.This document is for reference only and cannot be
C.The minimum thickness of the polyethylene sheath is used as an attachment to the contract.For detailed
1.5mm.product information,please contact our sales staff.













